| HOME | MENU | DOCS | SEARCH |
Translations of articles in the English language
is in automatic mode, the original version
of the article in Russian - here
The content of the article "Evaluation of respiratory functions in sports":
The system of external respiration
The parameters of the respiratory system
Evaluation and trial of the functions of respiration
Breathing — is the process performed by the integral organism and consists of three inseparable parts: a) external respiration, i.e. gas exchange between the external environment and the blood in pulmonary capillaries; b) gas transport by the blood circulatory system; b) internal (tissue) respiration, i.e. gas exchange between the blood and the cell, where the cells consume oxygen and release of carbon dioxide (Fig. Functions of the respiratory system).
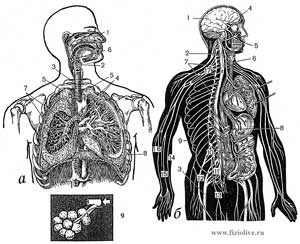
Functions of the respiratory system
The organs of the thoracic cavity (a). Peripheral and Central nervous system (b).
a: 1 — nasal cavity 2 — pharynx, 3 — trachea 4 — bronchi, 5 — apex, 6 — oropharynx, 7 — branches of the lower lobar bronchus, 8 — diaphragm, 9 — alveoli.
b: 1 — brain, 2 — spinal cord, 3 — sciatic nerve, 4 — optic nerve, 5 — facial nerve, 6 — vagus nerve 7 — the nodes of the sympathetic trunk, 8 is the solar plexus, 9 — intercostal nerves, 10 — lumbar plexus, 11 — sacral plexus, 12 — femoral nerve, 13 — obturator nerve, 14 — ulnar nerve, 15 is the median nerve, 16 — radial nerve, 17 brachial plexus.
The basis of tissue respiration is a complex oxidation-reduction reactions, accompanied by release of energy, which is necessary for the functioning of the body.
Human performance (in particular, the athlete) is mainly determined by the amount of oxygen (O2) taken from outside air in the pulmonary capillary blood and taken to tissues and cells. The above three respiratory system are closely linked and have a mutual compensation. Thus, in heart failure, dyspnea occurs, with a lack of O2 in ambient air (e.g. in the Midlands) increases the number of red blood cells — oxygen carriers, in diseases of the lungs occurs tachycardia.
The respiratory system consists of lungs, upper respiratory tract and bronchi, rib cage and respiratory muscles (intercostal, diaphragm, etc.).
Provides external respiration exchange of gases between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood, the venous blood saturation with oxygen and the release of excess carbon dioxide that indicates the relationship of respiratory function with regulation of acid-base balance.
In the physiology of respiration respiratory function is divided into three major processes — ventilation, diffusion and perfusion (the blood flow in the capillaries of the lungs).
Under the ventilation should understand the exchange of gas between alveolar and atmospheric air. The level of alveolar ventilation depends on the constancy of the gas composition of the alveolar air.
Alveolar ventilation is equal to the difference between the volume of breathing per minute and the volume of dead space, multiplied by the number of breaths per minute. The amount of ventilation depends primarily on the body's need for oxygen during injection of a certain amount of carbon dioxide, as well as the state of the respiratory muscles, patency of the bronchi, etc.
Not all inhaled air reaches the alveolar space where gas exchange occurs. If the volume of inhaled air is equal to 500 ml, 150 ml remain in dead space, and for a minute through the respiratory area of the lungs on the average passes (500 ml — 150 ml) x 15 (breathing rate) = 5250 ml of atmospheric air. This value is called the alveolar ventilation. Dead space increases with a deep breath, its volume depends on body weight and posture of the subject.
Diffusion — is a passive process of transfer of oxygen from the lungs through the alveolo-capillary membrane into the pulmonary capillaries hemoglobin, with which oxygen enters into chemical reaction.
Perfusion (irrigation) of the lungs by the blood through the vessels of a small circle. About the efficiency of the lungs is judged by the ratio between ventilation and perfusion. This ratio is determined by the number of ventilated alveoli that are in contact with well perfuziruemami capillaries. During quiet breathing in humans, the upper sections of the lung deal fuller than the bottom. In the vertical position, the lower sections of perfuziruemah blood is better than top.
Pulmonary ventilation is increased in parallel to the increased consumption of oxygen, and when maximum loads in trained individuals it can grow to 20-25 times in comparison with the rest and reach 150 l/min or more. This increase in ventilation is ensured by increasing the frequency and volume of respiration, and the frequency may increase to 60-70 breaths per minute and tidal volume from 15 to 50% vital capacity of the lungs (H. Monod, M. Pottier, 1973).
In the occurrence of hyperventilation during exercise plays an important role the respiratory center as a result of high carbon dioxide concentration and hydrogen ions at high levels of lactic acid in the blood.
Hyperventilation caused by exercise, always below the maximum ventilation, and an increase in diffusive capacity of oxygen in the lungs during the operation also is not limiting. Therefore, if there is no lung pathology, the breath does not limit muscular work. An important indicator is the consumption of oxygen reflects the functional state of the cardiorespiratory system. There is a relationship between the factors of circulation and respiration that affect the amount of oxygen consumed.
During exercise the oxygen consumption is significantly increased. This places high demands on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Therefore cardiorespiratory system is during muscular work subject to changes which depend on the intensity of physical activity.
The study of respiratory function in the sport along with the circulatory and blood to assess the functional status of the athlete as a whole and its backup capabilities.
The study started with the collection of medical history, then move to inspection, percussion and auscultation.
The examination allows to determine the type of breathing, to establish the presence or absence of shortness of breath (especially when testing), etc. Define the three types of breathing: thoracic and abdominal (diaphragmatic) and mixed. In the thoracic type of breathing to inhale significantly raises the clavicle and the movement of the ribs. With this type of breathing increases lung volume is mainly due to the movement of the upper and lower edges. Abdominal type of breathing increase in lung volume is mainly due to the movement of the diaphragm on inspiration it descends, thus shifting the several abdominal organs. Therefore, the wall of the abdomen on the inhale with abdominal type of breathing slightly protrudes. Athletes, as a rule, a mixed type of breathing, where participate both mechanisms increase the volume of the chest.
Percussion (tapotement) allows to determine the change (if any) the density of the lungs. Changes in the lungs are usually the result of some diseases (pneumonia, tuberculosis, etc.).
Auscultation (listening) determines the state of the Airways (bronchi, alveoli). In various diseases of the respiratory system are monitored very characteristic sounds — various rales, the strengthening or weakening of the respiratory noise, etc.
Study of external respiration is carried out by indicators of ventilation, gas exchange, the content and partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in arterial blood and in other settings. For the study of respiratory function using spirometers, spirographs and special machines open and closed. The most convenient spirographic study, in which on a moving paper tape is written to curve — spirogramma (Fig. Spirographic study). According to this curve, knowing the scale of the apparatus and the speed of the paper, define the following parameters of pulmonary ventilation: respiratory rate (ЧД), respiratory volume (ДО), minute volume of respiration (МОД), vital capacity (ЖЕЛ), maximum ventilation (МВЛ), residual volume of the lungs (ОО), total lung capacity (ОЕЛ). This paper also investigates the strength of respiratory muscles, bronchial patency, etc.
Spirographic study
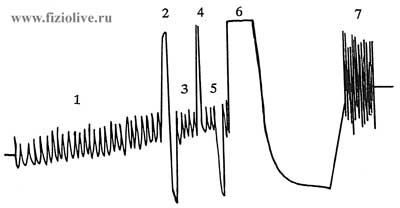
Spirogramma: 1 — МОД; 2 — ЖЕЛ, 3 — tidal volume (ДО); 4 — reserve volume of inhalation; 5 — expiratory reserve volume; 6 — sample Tiffno-Votchala; 7 — МВЛ
Pulmonary ventilation is linked to the function of the respiratory muscles (Fig. Emphysema). Movement of the lungs occur as a result of contraction of the respiratory muscles in combination with the movements of the parts of the chest wall and diaphragm. The respiratory muscles are those muscles, reduction which changes the volume of the thorax.
Emphysema
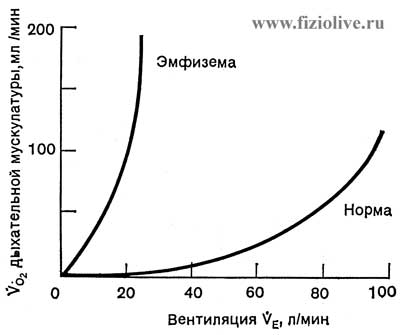
The oxygen consumption of the respiratory muscles in health and disease (emphysema)
Breath is created by expansion of the chest (cavity) and is always an active process. Usually the main role plays during inspiration the diaphragm. With enhanced inspiratory decrease extra muscle groups.
Breath at rest occurs passively due to the gradual reduction in muscle activity, creating conditions for inhalation. Relaxation associated with breathing muscle attached to the chest position of a passive exhalation. With a rapid exhalation, in addition to other muscle groups there are internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles.
Lung volume during inspiration is not always the same. The volume of air inhaled during a normal breath and exhaled during a normal breath is called air breathing (ДВ).
Residual air (ОВ) — volume of air remaining in nevozvrashchenija to the original position of the lungs.
Respiratory rate (ЧД) — number of breaths in 1 minute Definition of the black hole produced by spirogramma or by the movement of the chest. The average respiration rate in healthy individuals is 16-18 per minute, the athletes 8-12. At maximum load the BH grows to 40-60 in 1 min.
Depth of breathing (ДО) — the volume of air quiet expiration or exhalation during one respiratory cycle. The depth of respiration depends on the height, weight, gender and functional state of the athlete. In healthy persons is 300-800 ml.
The minute volume of respiration (МОД) describes the function of external respiration.
In the quiescent condition the air in the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and in repertoiremap the alveoli in gas exchange are not involved, since does not come into contact with an active pulmonary blood flow is the so — called "dead" space.
The portion of tidal volume that participates in gas exchange with pulmonary blood is called the alveolar volume. From a physiological point of view, alveolar ventilation is the most essential part of external respiration, as it is the volume inhaled in 1 min of air that exchanges gases with the blood of the pulmonary capillaries.
The МОД is measured by a ЧД ДО work on. In healthy individuals ЧД — 16—18 per minute, ДО and ranges from 350—750 ml, the athletes of the ЧД — 8—12 ml, ДО — increase the range of 900—1300 ml. МОД (hyperventilation) occurs due to the excitation of the respiratory center, shortness of oxygen diffusion.
Alone of МОД is 5—6 l, during intense exertion can increase 20-25 times and reach 120-150 l in 1 min or more. The increase in the МОД is directly dependent on the capacity of the work performed, but only to a certain point, after which the increase in strain is accompanied by increase in МОД.
Even with the heavy load МОД never exceeds 70-80% of the maximum level of ventilation. The calculation of the value of the МОД based on the fact that in healthy individuals from each liter of ventilated air is absorbed about 40 ml of oxygen (this so-called utilization factor of oxygen — KИ).
It can be calculated by the formula:
Should МОД = tribute oxygen consumption / 40
but should the magnitude of the oxygen uptake calculated by the formula:
needs basal metabolic rate (in kcal) / 7,07
where the main table is determined by the Harris-Benedict; 7,07 — the number obtained by multiplying the caloric value of 1 liter of oxygen (kcal 4,91) on the number of minutes in a day (1440 min) and divided by 1000.
Tables Harris-Benedict, to determine the basic exchange of the person:
The factor of age and height "Б"
Ventilation equivalent (ВЭ) are referred to as the ratio between the МОД and the amount of oxygen consumption. In the rest of 1 liter of oxygen absorbed in the lungs of 20-25 l of air. During heavy exercise ventilation equivalent increases and reaches 30-35 l. Under the influence of endurance training ventilation equivalent at a standard load is reduced. This indicates more effective breathing in trained individuals.
Vital capacity of lungs (ЖЕЛ) consists of respiratory lung volume, inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume. ЖЕЛ depends on sex, age, body size and fitness. ЖЕЛ is in average 2.5 to 4 l, and in males and 3.5—5 l. Under the influence of training ЖЕЛ increases, well-trained athletes it reaches 8 l.
The absolute values of ЖЕЛ are little informative because of individual variations. When evaluating the condition of patient it is recommended to calculate the "proper" value.
To calculate ЖЕЛ formula used is usually Anthony and Vernath (1961), based on the size of the basic exchange (kcal/24 h). It can be found on the tables of Harris-Benedict, respectively sex, age and body weight.
ДЖЕЛ = value of basal metabolism (kcal) х K,
where K — factor: 2,3 in women and 2.6 in men. The amount of basal metabolism (kcal) determined from the tables of Harris-Benedict, where they find the growth factor (Б) and the weight factor (А). The sum А + Б is have the value of the main exchange. Should the main exchange, and how ЖЕЛ, depends on sex, age, height and weight, can easily be determined by special tables and is expressed in kilocalories. To Express the relationship in percentage of the actual ЖЕЛ needs to use the formula:
(actual ЖЕЛ / due value ЖЕЛ) х 100
ЖЕЛ is considered normal if is 100% value. For the assessment of ДЖЕЛ you can use the nomogram (Fig. Evaluation of lung capacity; Vital capacity of lungs). ЖЕЛ is expressed as percentage by ДЖЕЛ.
Evaluation of vital capacity of the lungs
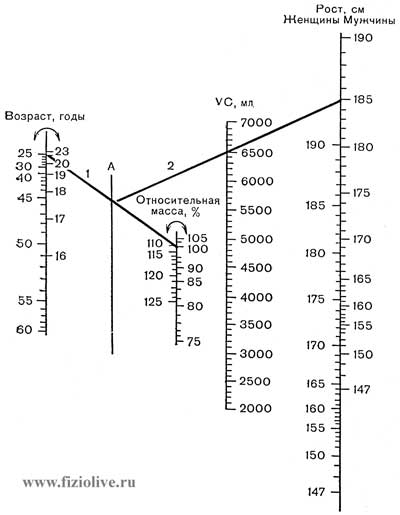
Nomogram for estimation of vital capacity of lungs (VC, ml). Connecting by a straight line (1) corresponding points on the scales "Age" and "relative mass", on line a, mark the point of intersection. From this point draw line (2) on a scale of "Growth". The point of intersection with the scale and VC will have a value of vital capacity of the lungs (ДЖЕЛ). The limits: х(2) = 1200 ml (Amrein et al., 1969)
Vital capacity of lungs

Nomogram for determination of the vital capacity depending on height and age
Total lung capacity (ОЕЛ) represents the sum of ЖЕЛ and residual volume of the lungs, the air that remains in the lungs after a maximum expiration and can only be determined indirectly. In young healthy individuals — 75-80%. ОЕЛ is ЖЕЛ, and the rest is residual volume. In athletes the share of the ЖЕЛ in the structure of ОЕЛ increases, which favorably affects the efficiency of ventilation.
Maximal voluntary ventilation (МВЛ) — is the maximum possible amount of air that can be ventilated through the lungs per unit time. Usually forced respiration is carried out for 15 s and multiplied by 4. This will be the biggest international airlines МВЛ. Large fluctuations of local airlines reducing the diagnostic value of determining the absolute values of these quantities. Therefore, the value obtained should lead to international airlines. To determine the МВЛ should use the formula:
should МВЛ = 1/2ЖЕЛ х 35,
or using the main exchange table A. Telecines (1968); or the nomogram (Fig. Estimate of maximum minute ventilation of the lungs).
Estimate of maximum minute ventilation of the lungs
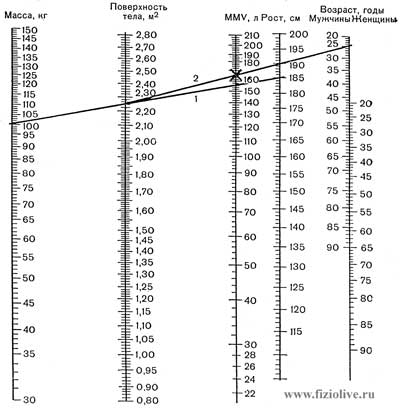
A nomogram to estimate maximum minute ventilation (MMV). Connecting by a straight line (1) corresponding points on the scales "weight" and "growth", find the point of intersection with the scale of "Surface body". Then this point connect direct (2) with the corresponding point on the scale of "Age" and on the intersection of this line with the scale of the MMV must find the value of the maximum ventilation (Amrein et al., 1969)
The reduction in МВЛ is due to the decrease in the volume of ventilated lung tissue, and reduce bronchial obstruction, inactivity. In men aged 20-30 international flights ranges from 100 to 180 (average 140 l/minutes), in women — from 70 to 120 l/minutes At tall sportsmen with well-developed breathing muscles МВЛ sometimes up to 350 l/minutes, sportswomen — 250 l/minutes (W. Hollmann, 1972).
Thus МВЛ most accurately and completely describes the function of external respiration in comparison with other spirographic indicators.
To assess bronchial patency use test ФЖЕЛ (forced vital capacity). Surveyed offer as deeply as possible to inhale and exhale quickly. ФЖЕЛ in healthy individuals below ЖЕЛ on 200—300 ml. Tiffno proposed measure ФЖЕЛ in the first second. Normal ФЖЕЛ per second is not less than 70% ЖЕЛ.
Pneumotachometry is a peak flow meter B. E. Votchala. Method of pneumotachometry determine the speed of the air stream in quickly inhale and exhale. In healthy individuals this ranges in men from 5 to 8 l/s, women — from 4 to 6 l/s. this dependence is pneumotachometry indicator from ЖЕЛ and age. Found that the more ЖЕЛ, the higher the maximum expiratory flow. Pneumotachometry figure depends on bronchial patency, strength of the respiratory muscles of an athlete, his age, sex and functional status.
The value of maximum expiratory flow compared with proper values, calculated by the formula:
should the value of expiration = ЖЕЛ х 1,2
The difference of actual and supposed quantities in healthy people should not be more than 15% of the proper level. In healthy individuals the rate of exhalation more than inhalation. With the increase of fitness were predominant maximum speed of inhalation over exhalation. Increase in the speed of breath in athletes due to the increased reserve capacity of the lungs.
Volume of air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation (ОО) most completely and accurately describes the gas exchange in the lungs.
One of the main indicators of external respiration is gas exchange (analysis of respiratory gases — carbon dioxide and oxygen in the alveolar air), i.e. the absorption of oxygen and excretion of carbon dioxide. Gas exchange external respiration characterizes the stage of "alveolar air — pulmonary capillary blood". He is investigated by gas chromatography.
Functional test of Rosenthal allows to judge about the functionality of the respiratory muscles. Test performed on the spirometer, where the surveyed 4-5 times in a row with an interval of 10-15 seconds, determine ЖЕЛ. Normal get the same performance. The decline of ЖЕЛ during the study indicates that fatigue of the respiratory muscles.
Pneumotonometry index (ПТП, mm mercury) allows us to estimate the strength of the respiratory muscles, which is the basis of the ventilation process. ПТП is reduced during inactivity, when long breaks in training, with fatigue, etc. the Research is conducted by pneumotonometry Dubrovsky and V. I. Deryabina (1972). Studied produces the exhale (or inhale) into the mouthpiece of the phone. In healthy individuals ПТП on average in men as you exhale 328 ± 17,4 mm mercury, on the breath — 227 ± 4,1 mm mercury, for women, respectively, were, — 246 ± 1,8 and 200 ± 7,0 mm mercury. With lung diseases, physical inactivity, fatigue, these indicators are decreasing.
During exercise, especially in cyclic kinds of sport (ski races, marathon running, rowing, etc.), the respiratory musculature is a limiting factor.
In Fig. Respiratory rate shown lung function at rest and muscular load. Total lung capacity during exercise can decrease due to the increase vnutritorakalnah blood volume. At rest respiratory volume (ДО) is 10—15% ЖЕЛ (450—600 ml), during physical activity can reach 50% ЖЕЛ. Thus, people with large tidal volume ЖЕЛ under the conditions of intensive physical work can be 3-4 l. As shown in Fig. Respiratory rate, ДО increases mainly at the expense of the inspiratory reserve volume. Expiratory reserve volume even with heavy physical activity varies slightly. As during physical work increases the residual volume and functional residual capacity is almost constant, and ЖЕЛ decreases.
Respiratory rate
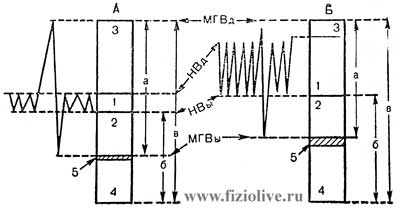
Lung function at rest (А) and maximum exercise (Б).
Respiratory rate (fR) 10—15 and 40—50 min-1 respectively 1 — tidal volume; 2 — expiratory reserve volume; 3 — reserve volume of inhalation; 4 — residual volume; 5 — vnutritorakalnah blood volume.
МГВд — maximum deep breath; НВд — normal breath; НВы — normal exhalation; МГВы — maximum deep expiration; а — vital capacity of the lungs; б — functional residual volume, в — total lung capacity [R. Margaria, P. Cerretelli, 1968]
Samples Stange and Genchi give some insight on the body's ability to withstand the lack of oxygen.
The Sample Rod. Measured maximum delay time of the breath after a deep breath. In this case the mouth should be closed and the nose pinched by fingers. Healthy people are holding their breath, on average, 40-50; highly skilled athletes up to 5 minutes, and athletes — from 1.5 to 2.5 minutes.
With the improvement of physical fitness as a result of adaptation to physical hypoxia, the delay time increases. Therefore, the increase of this indicator during re-examination is regarded (taking into account other indicators), as improving fitness (fitness) athlete.
Test of Genchi. After a shallow inhale, exhale and hold your breath. In healthy people, the time of delay of breathing is 25—30 с. Athletes are able to hold your breath for 60—90 с. In chronic fatigue is the time of delay of breathing is dramatically reduced.
The value of samples Stange and Genchi increases if to observe constantly, in the dynamics.
V.I. Dubrovsky,
Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences,
IANPO and the New York Academy of Sciences,
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor,
A.V. Dubrovskaya, pediatrician
It is available for the original version
of the article in Russian
<< Previous: sports, featured articles
We recommend that you look at the popular sections of the site myvaleology.com: MENU with a description of the sections | |||
| SOCIAL | DONATION | MY DIET | MY SPORT |

|
Release all4e8 |
||
Copyright © VZOJ 2023. All rights reserved. When reprinting or quoting myvaleology.com materials please put a link to the site myvaleology.com :
<a href="https://myvaleology.com">Healthy lifestyle</a>