| HOME | MENU | DOCS | SEARCH |
Translations of articles in the English language
is in automatic mode, the original version
of the article in Russian - here
The content of the article "exercise therapy in diseases of the cardiovascular system and joints":
Varicose veins of the lower extremities
*Initial position - I. p.
Cardiovascular system ensures the delivery to the tissues needed for their livelihoods nutrients, oxygen, and water as the continuous removal of products of metabolism by the moving fluid.
K the circulatory system include: heart functions as a pump, and peripheral blood vessels - arteries, veins, and capillaries (see Fig. Scheme of blood circulation). Emitted by the heart blood is carried to the tissues via arteries, arterioles (small arteries) and capillaries, and then returns to the heart via the venules (small veins) and veins large. In Fig. The distribution of blood flow in organs and tissues is a diagram of blood circulation in vital organs and systems at rest and during exercise.
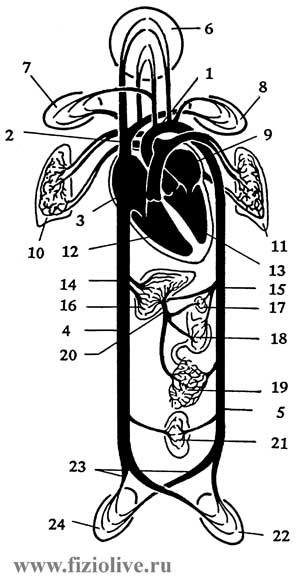
Scheme of blood circulation

1 - aorta; 2 - upper hollow Vienna; 3 - right atrium; 4 - lower hollow Vienna; 5 - descending aorta; 6 - vessels of the head and neck; 7 - vessels of the right upper limb; 8 - vessels of the left upper limb; 9 - the left atrium; 10 - vessels of the right lung; 11 - vessels of the left lung; 12 - right ventricle; 13 - left ventricle; 14 - hepatic vein; 15 - celiac trunk; 16 - liver; 17 - the spleen; 18, stomach; 19 - digestive tract; 20 - portal vein; 21 - kidney; 22 - vessels of the left lower extremity; 23 - iliac artery; 24 - vessels of right lower extremity
The distribution of blood flow in organs and tissues
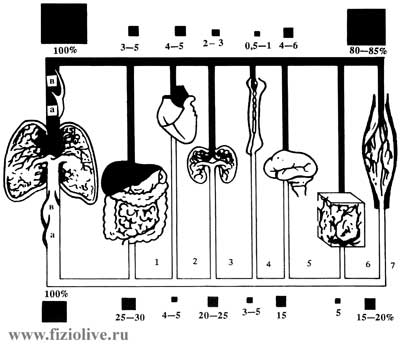
The distribution of blood flow in organs and tissues at rest and during exercise (P.-O. Astrand, K. Rodahl, 1970).
Top line: the Hard work of the МОС - 25 l/min
Bottom line: the Rest of the МОС is 5 l/min
The disease is the functional narrowing of the arterioles. This is due to increased tone of the smooth muscles of the arterial walls.
Hypertension is a chronic disease. The main symptom is high blood pressure, with periodic upgrades, sometimes accompanied by subjective sensations associated with quickly passing cerebral (brain) vasospasm (vessel spasm).
Note: I. p. - initial position; TM - the pace is slower; TA -the average pace.
Approximate complex LH in hypertension
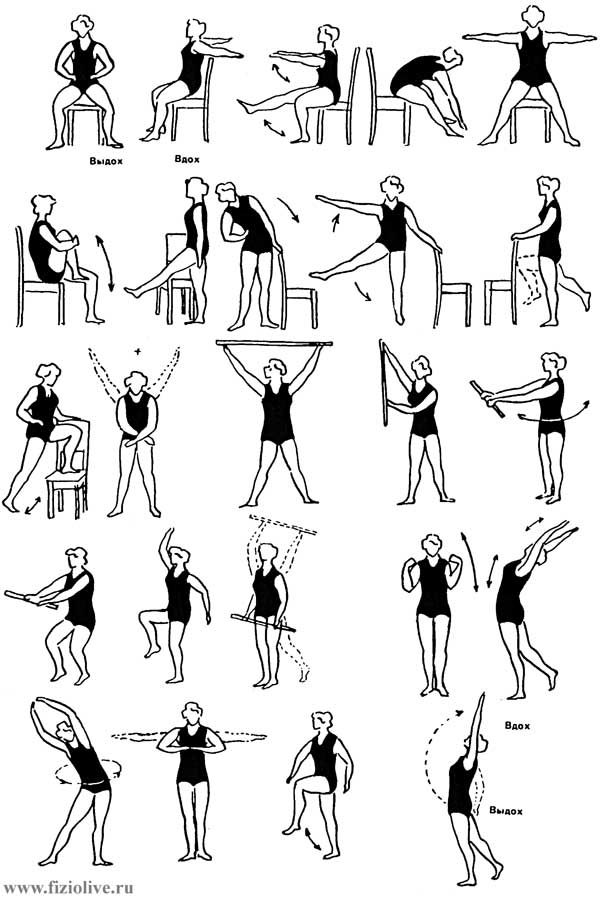
1. I. p. - sitting on a chair, hands on his belt. Hands in sides; to return to I. p. 4-6 times. TC. Breathing evenly.
2. I. p. - the same. Hands forward, to straighten the right leg; return to The same I. p. with his left foot. 3-5.
3. I. p. - sitting, hands to the shoulders. The forward bend - exhale; return to I. p. - breath. 4-6 times. TC.
4. I. p. - the same. Stand up, arms at sides - inhale; sit up, exhale. 3-5. TM.
5. I. p. - sitting. Bend the right leg, clasping her hands; to return to The same I. p. with his left foot. 3-5. TM.
6. I. p. - standing by the chair. In turn the lead foot forward. 5-7 times. TC.
7. I. p. - the same. Tilts right or left. 5-7 times.
8. I. p. - the same. The retraction of the legs and arms to the side. 5-7 times. TC.
9. I. p. - the same. Alternately bending the legs at the knee and hip joints. 4-6 times on each leg. TC.
10. I. p. - standing. Step left foot on a chair; to return to The same I. p. with his right foot. By 5-7 times. TM.
11. I. p. - standing. Hands up - inhale, bend forward; hands down - exhale. 4-6 times. TC. Breathing evenly.
12. I. p. - the same. Exercises with gymnastic stick. Hands up - inhale, hands down - exhale. 5-7 times. TC.
13. I. p. - standing, hands in front of chest. Turns left and right. 4-6 times. TC.
14. I. p. - standing. Sit down - hands forward; to return to I. p. 5-7 times. TC.
15. Walking with high raising knees. Breathing evenly.
16. I. p. - standing. Alternate the lead foot forward and hands up. Hands up - inhale, hands down - exhale. 4-6 times. TC.
17. I. p. - standing, hands to the shoulders. Take leg back, hands up - inhale; return to I. p. exhale. 5-7 times. TM.
18. I. p. - standing, hands at the top of "the castle". The rotation of the torso. 4-8 times. TM.
19. I. p. - standing, hands in front of chest. Abduction hands to the sides. 5-7 times. TC.
20. I. p. - standing. Walking with high raising knees. 30 S. TM.
21. I. p. - standing. Hands up, right foot to take back the breath; to return to I. p. exhale. The same with the left foot. 6-8 times. TC.
22. Walking around the room - 30-60 s. Breathing evenly. TC.
Vascular hypotension develops as a result of lowering the tone of the medium and small arteries caused by dysfunction of vascular tone regulating apparatus.
When hypotonic disease may experience frequent dizziness, fatigue, easy excitability of cardiac activity, sometimes pain in the heart, etc. Blood pressure is lowered (to 80/40 mm Hg. calendar). Sometimes experience periods of sharp deterioration (crises) which increase General weakness, dizziness, fatigue more pronounced.
In case of hypertensive disease shown exercise (walking, Jogging, skiing, Cycling, games, etc.), daily morning hygienic exercises, including exercises in isometric mode, with dumbbells, rubber elastic bandage, etc., tempering procedures (contrast shower, massage massagers, etc.).
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is an acute or chronic heart damage associated with reduction or cessation of blood delivery to the myocardium due to the pathological process in the coronary (heart) arteries. The mismatch of coronary blood needs of the myocardium may also be due to spasm of the coronary vessels of psycho-emotional, reflexive, and others.
Effective method of preventing coronary heart disease, in addition to a balanced diet, are moderate exercise (walking, Jogging, skiing, tourism, Cycling, swimming) and daily morning exercises. Should not get involved in heavy lifting (weights, big dumbbells, etc.) in the morning to do long runs (over an hour), causing severe fatigue. Need hardening.
Approximate complex LH in ischemic heart disease
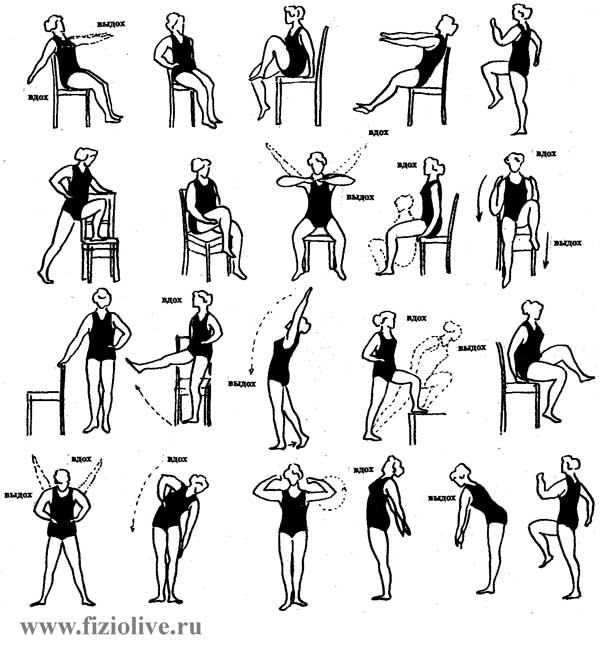
1. I. p. - standing on the seat of the chair, hands on his belt. To take arms at sides - inhale; hands on the waist - exhale. 4-6 times. Breathing evenly.
2. I. p. - the same. Hands up - inhale, bending forward, exhale. 5-7 times. TC.
3. I. p. - standing, hands in front of chest. To take arms at sides - inhale; return to I. p. exhale. 4-6 times. TM.
4. I. p. - standing by the chair. Sit down - exhale; to take breath. 5-7 times. TM.
5. I. p. - sitting. Bend the right leg - cotton; to return to I. p. The same with the other leg. 3-5. TC.
6. I. p. - sitting on a chair. Sit down in front of the chair; to return to I. p. Breath not to detain. 5-7 times. TM.
7. I. p. - legs should be straight, hands in front. To bend feet in knees, hands on a belt; to return to I. p. 4-6 times. TC.
8. I. p. - standing. Take the right leg back, hands up - inhale; return to I. p. exhale. The same with the left foot. By 4-6 times. TM.
9. I. p. - standing, hands on his belt. The slopes of the left and right. By 3-5 times. TM.
10. I. p. - standing, hands in front of chest. To take arms at sides - inhale; return to I. p. exhale. 4-6 times. TC.
11. I. p. - standing. Take the right leg and arm forward. The same with the left foot. By 3-5 times. TC.
12. I. p. - standing, hands up. Sit down; return to I. p. 5-7 times. TC. Breathing evenly.
13. I. p. - the same, hands up, hands "in lock". The rotation of the torso. 3-5. TM. Breath not to detain.
14. I. p. - standing. Step with left foot forward, arms up; to return to The same I. p. with his right foot. By 5-7 times. TC.
15. I. p. - standing, hands in front of chest. Turns left or right with the breeding of hands. 4-5. TM.
16. I. p. - standing, hands to the shoulders. Turns to straightening of hands. 6-7 times. TC.
17. Walking in place or around the room - 30 seconds Breathing evenly.
Approximate complex vestibular gymnastics
(in Meniere's disease, arachnoiditis, hypertension and other pathologies associated with impaired vestibular function)
Starting position lying down:
1. Put your hands up - inhale, down - exhale. 3-5.
2. The same. To your eyes follow hand movements. 4-6 times.
3. Moving the legs ("walk" while lying). To breathe freely. 30-40 s.
4. Head movement up and down, accompanying the look. 4-6 times.
5. Alternate lead legs to the side. 5-6 times. Breath not to detain.
6. Take turns to lift the arm up and lower down. To follow the movements of the hands. By 5-7 times.
7. Take the left arm up and bent at the knee right leg. The hand movement to accompany the look. The same with the other arm and leg. By 5-7 times.
8. Turning his head left and right. 3-5 times in each direction.
9. Hands forward. Flexion and extension in the elbow joints, the compression and uncompression of the fingers. Eyes to monitor the movements of your fingers. 5-8 times.
10. Hands up - inhale, down - exhale. Breathing freely 30 seconds.
11. Turning his head left and right, the chin touch the shoulder. 5-7 times.
12. Hands up - inhale, down - exhale. To breathe freely. 30 s.
The original sitting position:
1. The head is lowered. Slow ambulation and lifting the head. 3-5.
2. Hands forward. Alternately diverted to one side. Look to accompany the hand movements. 3-5 times with each hand.
3. Slow head turns to the side and rotate it. 5-7 times.
Starting position standing:
1. To get out of the chair to rotate 360° and to sit down. Turns to run left, then right. 3-5 times in each direction.
2. Standing at the chair, take your hand to the right, accompanying the abstraction view. The same in the other direction. 5-7 times in each direction.
3. Hands up, put down and take up the seat of the chair. 5-7 times.
4. Walking in a straight line, hands forward (watch the hands), walk through obstacles and zigzag - 1 min.
In subsequent sessions more difficult. Include exercises with balls, gymnastic sticks, gymnastic wall (with the inclusion of exercises with a turn of the head, bending the torso), on the gymnastic shield with a raised head end or Vice versa. Complicated and exercise at the walk: include walking in a straight line, hands in front, to the sides, on the belt; with the raising of the knee (see knee, then forward, etc.); eyes closed (straight, zigzag). In later recommended the game in table tennis, skiing and other sport activities.
Arthritis is a chronic disease of joints that causes degenerative changes in the articular cartilage. In the initial phase of development, rapidly advancing disease is characterized by fatigue in the joint, dull or aching pain. They are caused, apparently, by reflex changes in the muscles, blood circulation, etc. the Cause of arthritis are microtrauma, systemic effects of overload, hypoxia, impaired innervation, tissue, damaged cartilage, etc.) With osteoarthritis of the recommended cryo, LH, hardening, skiing, Cycling, boating, sauna (bath), shared massage, etc. are Excluded exercises with dumbbells, kettlebells, jumping, jumps, squats, etc. in the original standing position.
Exercises in deforming arthrosis (hip and knee joints)
1. I. p. - lying on his stomach, holding his hands over the rail. Pulling up turns feet m the stomach. By 3-5 times.
2. I. p. - the same. Abstraction turns legs apart. By 3-5 times.
3. I. p. - the same. The rotation of the leg at the knee joint. 3-5 times in each direction.
4. I. p. - lying on his back, holding the rim with your hands. Alternately bending the legs at the knee and hip joints. By 3-10 times.
5. I. p. - sitting in the pool, the emphasis behind. To bend, return to I. p. 5-10 times.
6. I. p. - sitting in the pool. Secure rubber elastic bandage at the side. Flexion and extension of hands in elbow and shoulder joints. 5-15 times.
7. I. p. - the same. The rotation of the arms in the shoulder joints. 5-15 times back and forth.
8. I. p. - the same. Turning the torso to the side. 5-10 times in each direction.
9. Crawl swimming on the chest and back.
Approximate complex LH in cases of arthritis and arthrosis

Arthritis is one of the most frequent manifestations of diseases of the joints. Characterized by mucous bags, ligaments, tendons, especially in the attachment of them to the bones, etc. In case of pain swelling in one or more joints develop contractures, muscle atrophy, etc.
Deforming arthrosis - a chronic disease related to arthritis, it is based on a degenerative process in the joint (the articular cartilage is damaged and the edges of the joint there is a bone overgrowth). Deforming arthrosis is more common in athletes, manual workers and the elderly due to micro-traumas, tissue malnutrition, hypothermia, etc. usually Affects a single large joint, most often the knee and hip. Gradually there is a slight pain and a little awkward in the affected joint without any objective changes. These symptoms slowly progress, the function of a joint is deteriorating.
Prophylactic and therapeutic use means of physical culture (walking, Cycling, skiing, swimming, etc.) and hardening.
When deforming arthrosis should not run, jump and perform other exercises that cause additional trauma to (the load) on the joint. During exacerbation of physical education and tempering are not performed. Shown morning hygienic gymnastics lying, sitting and standing. Good effect swimming and running in the pool (tub) different exercises. Shown a massage (massage) joints (stroking, rubbing), petrissage of the muscles located above and below the joint. If there are no contraindications (from other bodies), it is recommended hyperthermic bath (38-41°C for 5-10 min).
Approximate complex LH in polyarthritis
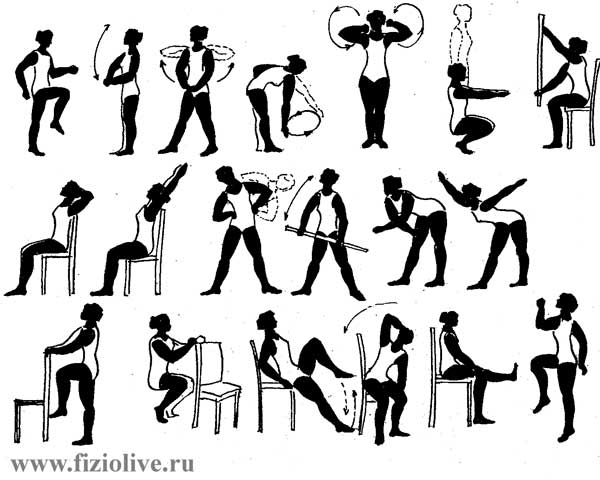
1. Walking in place or around the room. TC. 15-30 s. Breathing evenly.
2. I. p. - standing, hands "in lock". Retraction of the arms up and down. TC. 5-7 times.
3. I. p. - the same. Hands to the shoulders - inhale, return to I. p. exhale. TM. 6-8 times.
4. I. p. - standing, tilt, left hand on the belt, the rotation of the arm at the shoulder. The same with the other hand. TC. 6-8 times with each hand.
5. I. p. - hands to the shoulders. The rotation of the hands back and forth. TC. 5-7 times.
6. I. p. - standing. Sit down - hands forward. TM. 4-6 times.
7. I. p. - sitting. Exercises with gymnastic stick. Hands forward. Turns left and right. TM. 5-7 times in each direction.
8. I. p. - sitting, hands behind his head. Turns left and right. TC. 6-8 times.
9. I. p. - sitting, hands to the shoulders. Hands up - inhale; return to I. p. exhale. TC. 5-7 times.
10. I. p. - standing, hands on his belt. The slopes of the left and right. TM. 6-8 times in each direction.
11. I. p. - standing, hands down. To rise on socks - hands up (breath), return to I. p. exhale. TM. 4-6 times.
12. I. p. - trunk in the slope. Abduction hands to the sides, inhale. Hands strastno (hugging yourself) - exhale. TC. 5-8 times.
13. I. p. - standing by the chair. To raise knees. TC. 6-8 times each leg.
14. I. p. - the same. Squat. TM. 5-7 times.
15. I. p. - sitting. By turn bending of feet. TC. 6-8 times each leg.
16. I. p. - sitting, hands down. Tilt left - right hand behind your head. The same in the other direction. TC. 5-7 times in each direction.
17. I. p. - sitting. Straighten the left leg at the knee and produce flexion, extension and rotation. The same with the other leg. TC. 6-8 times each leg.
18. Walking in place or around the room. TC. 15-30 s. Breathing evenly.
Varicose veins of the lower extremities - saccular or cylindrical dilation of the subcutaneous veins of the extremities, accompanied by failure of valves and improper blood flow.
The patient has a feeling of heaviness and enlargement in the legs during prolonged standing, seizures. In the later stages of edema, pigmentation and induration of the skin in the inner ankle, then in this zone appears trophic ulcer, etc.
Varicose veins of the lower extremities is one of the causes of chronic venous insufficiency, which impaired outflow of venous blood from the affected limb.
The disease affects primarily those who are engaged in physical labor, work standing (dentists, hairdressers, etc.), athletes, women in the second half of pregnancy. the Treatment is conservative. Wearing elastic stockings (or bandaging), physical therapy, segmental massage (V. I. Dubrovsky), swimming, etc. for varicose veins of the lower extremities in pregnant women is performed physiotherapy in the supine position on the couch with the footboard, a raised angle of 15-25°. Shown back massage and diploid (suction) foot massage, contrast showers, moderate walking. From the diet excluded salty meals, limit the amount of fluid intake.
The causes of the disease are the prolonged work sitting or standing, strenuous exercise, constipation, abuse of spicy food, alcohol, etc. Characterized by the selection of red blood, pain and prolapse out during bowel movements, you may intermittently receive an acute inflammation and thrombosis nodes, itching.
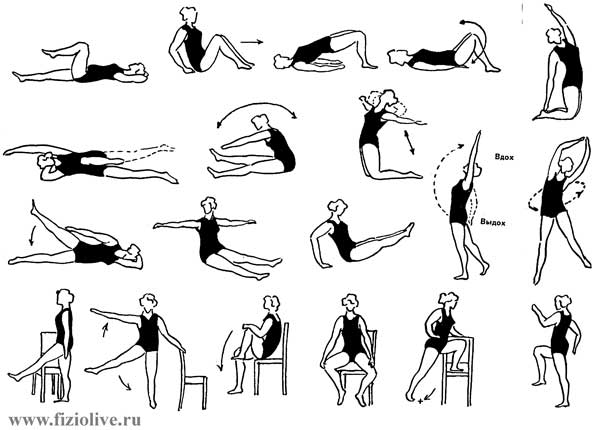
Hemorrhoids shown LH (see Fig. An approximate complex of therapeutic exercises for hemorrhoids), hardening, swimming, skiing, sauna (sauna), diet, fortification, sitting cool baths, anti-inflammatory candles, etc.
Approximate complex LH hemorrhoids
V.I. Dubrovsky,
Academician of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences,
IANPO and the New York Academy of Sciences,
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor,
A.V. Dubrovskaya, pediatrician
It is available for the original version
of the article in Russian
<< Previous: Exercise therapy for injuries and diseases
We recommend that you look at the popular sections of the site myvaleology.com: MENU with a description of the sections | |||
| SOCIAL | DONATION | MY DIET | MY SPORT |

|
Release all4e8 |
||
Copyright © VZOJ 2023. All rights reserved. When reprinting or quoting myvaleology.com materials please put a link to the site myvaleology.com :
<a href="https://myvaleology.com">Healthy lifestyle</a>